Meniscus Tears and Treatment:
The knee is the largest and moving joint of the body. Collateral and cruciate ligaments provide the suitability of the knee.
There are cartilaginous structures in the body between the femur and the tibia called meniscus. The meniscus is located in medial and lateral parts of each knee in a semilunar or C shaped.
Meniscuses increase the compatibility between the femur and the tibia and play a role in balancing body weight in the knee joint and reducing the shock absorption.
In the absence of menisci, the joint surfaces between the thigh bone and the tibia are not perfectly aligned with each other, so the load will increase excessively at certain points and the load at the other points will not be distributed. In this case, it is inevitable to encounter a problem of early wear and osteoarthritis in the load bearing regions. Therefore, it is ant that the meniscus can function in terms of knee health.
Figure 1: Meniscus Tear Varieties
Meniscuses are often damaged by trauma in young athletes. However, tears caused by degeneratıon of menisci seen in elderly are not uncommon.
The most common mechanism is the rotation of the fixed body on the knee.
Anterior cruciate ligament injuries and collateral ligament injuries may occur together with meniscus tears and should be evaluated together for treatment.
The first signs of meniscal tear are pain and swelling. Locking in the knee meaning of no flexıon and extensıon of the knee is a detectable event and indicates that the torn meniscus interferes the joint movements.
Pain by pressure on the meniscus, crepitation during movements of the joints, and limited movement of the knee are other possible symptoms.
Every patient with a knee pain should be evaluated for meniscus tear. A good patient story and knee examination allows meniscal tears to be easily determined from other knee problems.
Knee X-ray and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are the most commonly used diagnostic tools. Knee x-ray is used to evaluate arthritis and related changes in the knee. MRI is quite valuable for meniscus imaging. However, the fact that only the MRI scans the meniscus is not enough to make a decision of arthroscopy alone.
In every knee injury, cold treatment, resting and immobilization should be done in the early period. Painkillers are used to relieve the patient and reduce the amount of edema.
The second step is to decide whether the patient needs surgery or not for meniscus rupture.
Surgery should be considered if the meniscus tears are painful and affects daily life.
There are two options that can be applied frequently to the meniscal tear:
Meniscus Repair: It is possible to repair the meniscus according to the shape of the tear. Not all patients are eligible for repair. Arthroscopic repair is possible. However, the process of healing is longer than that of patients with removal of meniscus (meniscectomy).
Meniscectomy: It is the method by which the torn part of the meniscus is removed. The meniscus is applied in the internal tears, which have no chance of healing. When done arthroscopically, there is a very rapid healing process and the patient can get up in the same day.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear and Treatment:
Cruciate ligaments connect the thigh (femur) and tibia bone through the knee joint like a short rope. They provide the necessary stability when the knee is bent and straightened. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is at the front and the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is at the back.
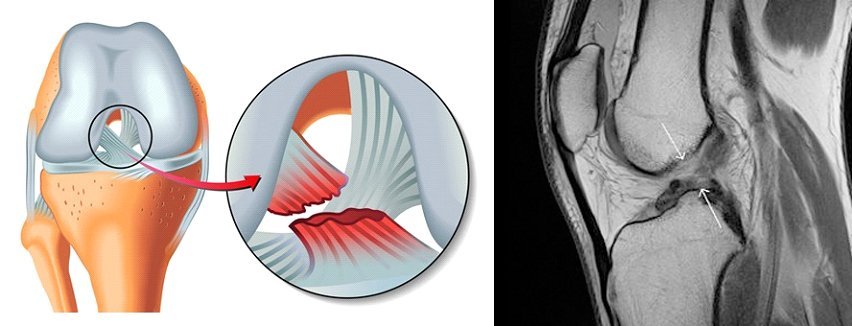
Figure 2: Anterior Cruciate Ligament tear
Anterior cruciate ligament can be injured in the following forms;
Sudden change of direction, knee rotation
Running, decreasing of movement speed while skiing,
Landing after jumping,
Direct damaged to the knee
When there is a trauma defined in the knee, the activity (sports, walking, etc.) absolutely must be ended.
Cold compress application with an ice pack around the knee should be done for 20 minutes and continued every 2 hours.
The patient should be evaluated by orthopedician and traumatologist and should not be allowed to bear weight to damaged knee until diagnosis by MRI(Magnetıc Resonance Imagıng)
The diagnosis can only be made after the examination and the gold standard MR imaging has been performed.
Non-Surgical Treatment
• Incomplete (partial) tears,
• People with old age or generally low physical activity,
•ıf the overall stability is good ın the stability tests such as the pivot shift test
surgical treatment may not be required for the knees.
It is recommended that such patients should regularly perform strengthening exercises for quadriceps and hamstring muscles, and use special knee braces in risky activities.
Surgical Treatment;
Patients who are active and want to play sports and patients with anterior cruciate ligament tear should be operated. Patients with low activity life operation may be planned due to feel confident while walking or to prevent cartilage injury.
Surgical treatment usually involves arthroscopically using a tendon (or a piece of tendon) around the knee to provide a reconstruction appropriate to the original anatomy of the anterior cruciate ligament.
Anterior cruciate ligament surgery is a low complication rate surgery when performed by experienced surgeons.
However, the most ant factor determining the future of the patient is the condition of other accompanying injuries, such as meniscus, cartilage.
Other than the general operative risks, complications in low rates can be seen such as infection, deep vein thrombosis (blood clot) and inadequate healing of the bone to the ligament; even if this technique is performed well.
On the next day of surgery, the patient can walk with two canadiens as the patient allows weight bearing.
Patients with desk job can start to work in 4-7 days.
They can start driving after 3 weeks.
If physiotherapy starts immediately after the surgery, it is aimed to walk with one canadian at the end of 2 weeks and to walk without any aid at the end of the third week.



